Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs): Benefits, Types, and Best Practices
Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) are redefining how warehouses and distribution centers move materials. Unlike traditional automation, AMRs use advanced sensors and AI to navigate dynamically, making them highly flexible in modern operations. As labor shortages and demand for faster fulfillment grow, AMRs offer a scalable and cost-effective solution.
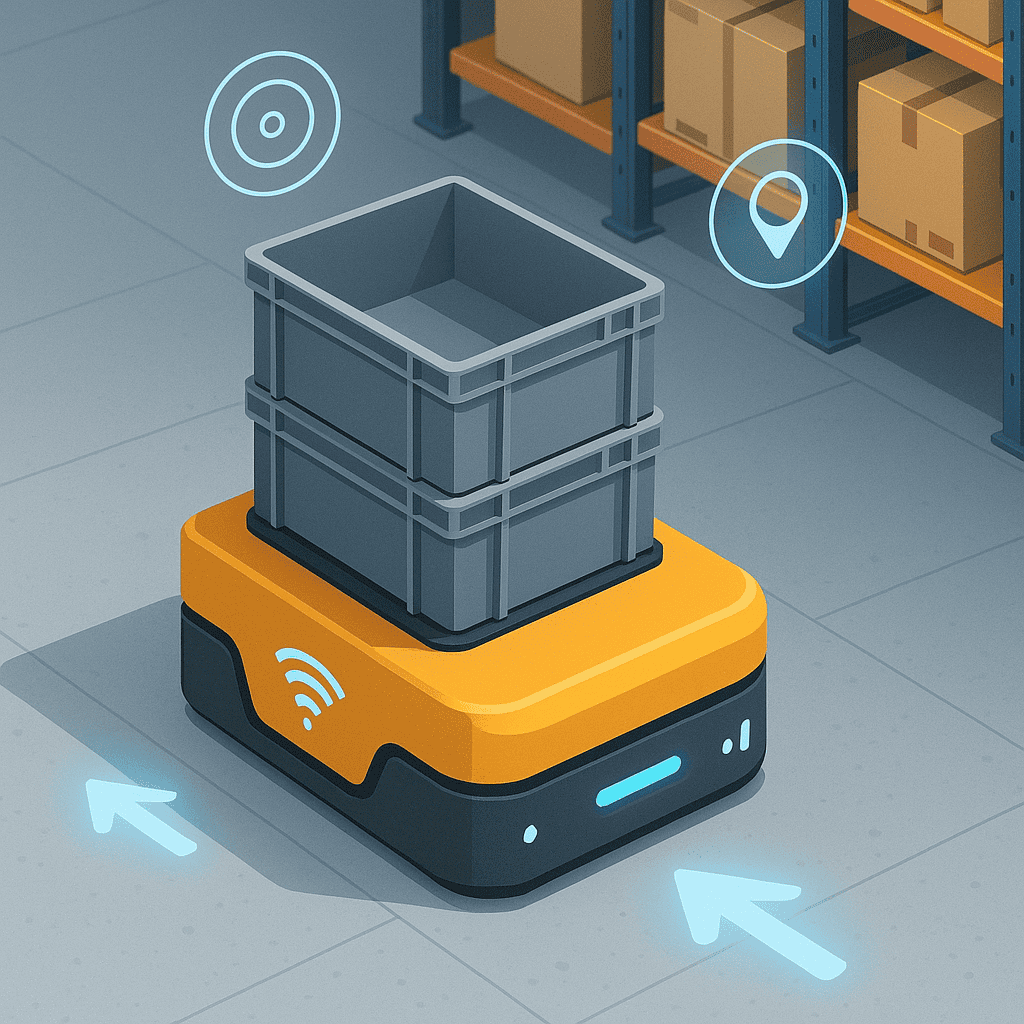
What are Autonomous Mobile Robots?
AMRs are self-navigating robots that transport goods across warehouse floors. They differ from Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs), which follow fixed paths. Instead, AMRs utilize LiDAR, cameras, and AI to detect obstacles and re-route in real-time, enabling them to work safely alongside humans.
Benefits of Autonomous Mobile Robots
Increased Flexibility
AMRs adapt to layout changes and do not require fixed infrastructure like magnetic tape or wires.
Reduced Labor Costs
By handling repetitive transport tasks, AMRs allow employees to focus on higher-value work.
Enhanced Safety
Sensors and obstacle-avoidance systems minimize accidents and collisions.
Faster Order Fulfillment
AMRs reduce travel time between picking and packing areas, speeding up order cycles.
Scalable Growth
Businesses can start small and add more AMRs as operations expand.

Types of Autonomous Mobile Robots
Goods-to-Person Robots – bring shelves or totes to pickers.
Shelf-Transport Robots – move entire shelving units.
Tote/Cart AMRs – handle smaller loads in fulfillment centers.
Hybrid AMRs – combine mobility with robotic arms for picking or kitting.
AMR vs. AGV: Key Differences
AGVs: Fixed-path navigation (wires, tape, lasers).
AMRs: AI-driven, dynamic navigation.
Result: AMRs provide more flexibility, while AGVs excel in highly structured environments.
👉 Related blog: Automated Guided Vehicles
Best Practices for Implementing AMRs
Start Small – pilot in a single department or workflow.
Integrate with WMS/WES – ensure robots align with order priorities.
Train Employees – staff must know how to work safely alongside AMRs.
Monitor ROI – track throughput, labor reduction, and downtime.
Plan for Maintenance – Proactive servicing keeps fleets running smoothly.
Costs & ROI
Cost Range: AMRs typically range from $20,000 to $100,000, depending on their complexity.
ROI Timeline: Many facilities recover costs in 2–3 years through labor savings, improved safety, and higher throughput.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Failing to integrate AMRs with WMS/TMS.
Underestimating employee training needs.
Ignoring facility layout adjustments for smooth navigation.
Deploying too many robots without testing workflows first.
FAQs
What industries use Autonomous Mobile Robots?
AMRs are used in e-commerce, retail, automotive, healthcare, and manufacturing.
What’s the difference between AMRs and AGVs?
AGVs follow fixed paths, while AMRs navigate dynamically with sensors and AI.
Can AMRs work with existing warehouse systems?
Yes. Leading AMRs integrate with WMS, WES, and even ERP systems for seamless operations.
How safe are AMRs?
AMRs are equipped with obstacle-detection sensors, making them safe to operate alongside human workers.
What is the future of AMRs?
Expect tighter AI integration, predictive routing, and collaboration with robotic arms for advanced picking tasks.
Additional Resources
Definition / Introduction
🔗 MHI: Mobile Robotics Overview – Industry association resource on AMRs.
Benefits & Trends
🔗 McKinsey: Automation and the Future of Warehousing – Covers efficiency and labor impact of robotics.
AMR vs. AGV
🔗 Robotics Business Review: AGV vs. AMR – Detailed comparison between AMRs and AGVs.