7 Predictive Maintenance Benefits Warehouses Can’t Ignore
Predictive maintenance is transforming how warehouses manage equipment, from conveyors to forklifts. Instead of waiting for breakdowns or relying on scheduled checks, predictive maintenance uses IoT sensors, machine learning, and data analytics to detect issues before they cause downtime. The result? Lower costs, higher uptime, and safer operations.
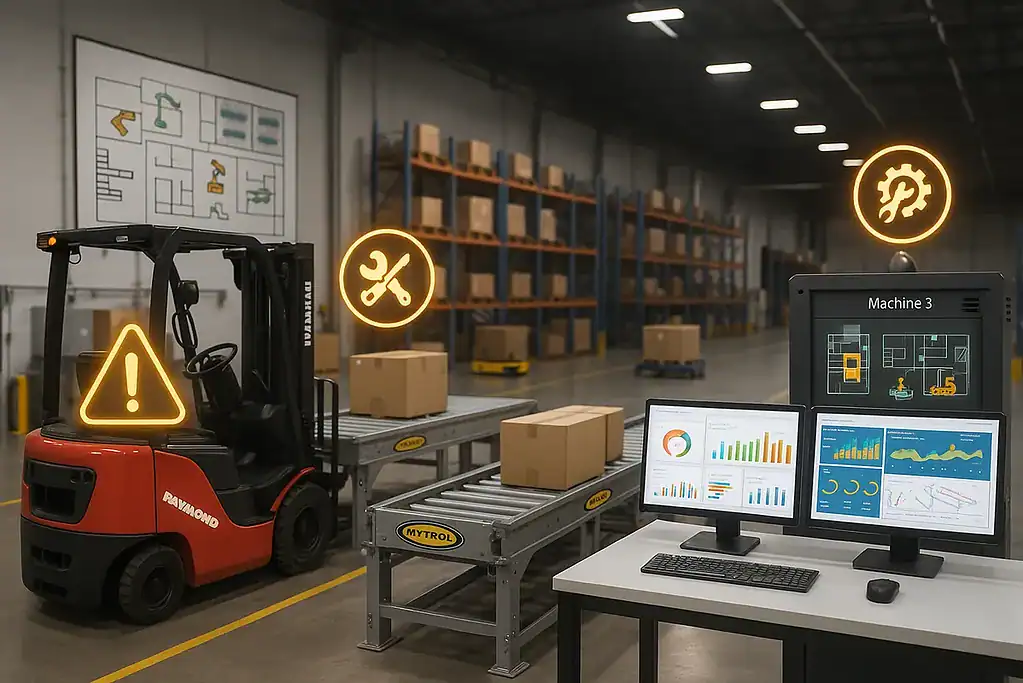

What Is Predictive Maintenance?
Predictive maintenance is a proactive strategy that monitors the condition of equipment and uses real-time data to anticipate when repairs are needed. By analyzing vibration, temperature, usage hours, and other data points, warehouses can prevent failures before they happen.
Predictive Maintenance Benefits
1. Reduced Downtime
By predicting issues before breakdowns, warehouses minimize equipment downtime and keep operations running smoothly. Equipment can be repaired during planned lulls, reducing the element of surprise and disruption.
2. Lower Maintenance Costs
Instead of replacing parts on a fixed schedule, repairs are done only when needed—saving money on unnecessary service. This prevents wasted spending on still-healthy components and allows maintenance budgets to stretch further.
3. Extended Equipment Life
Monitoring forklifts, conveyors, and AS/RS systems helps identify small issues early, preventing major wear and extending the lifespan of expensive assets. Early intervention means machines operate within safe parameters longer, avoiding premature replacement.
4. Improved Worker Safety
Malfunctioning equipment can create dangerous conditions. Predictive analytics reduces accidents by keeping machinery in top condition. When equipment runs reliably, employees can focus on their tasks without worrying about sudden failures.
5. Increased Inventory Accuracy
When equipment functions reliably, processes like picking, packing, and putaway remain accurate and consistent. A stable flow of operations reduces errors that creep in when systems fail or work is rushed.
6. Better Planning and Scheduling
Predictive models forecast when downtime is likely, enabling managers to schedule repairs during periods of low volume. This coordination prevents unexpected shutdowns and ensures customer orders remain on track.
7. Data-Driven Decision Making
Predictive maintenance establishes a data loop that feeds into broader warehouse data analytics, enabling leaders to improve efficiency across the supply chain. Managers gain confidence making long-term decisions when they’re supported by accurate, real-time insights.
Predictive maintenance creates a data loop that feeds into broader warehouse data analytics, helping leaders improve efficiency across the supply chain.

Challenges of Implementing Predictive Maintenance
Upfront investment: IoT sensors and software require capital.
Integration issues: Connecting new systems with legacy equipment.
Training needs: Staff must learn how to interpret predictive alerts.
Data quality: Inaccurate or missing sensor data can create false alerts.
Real-World Applications
Amazon uses predictive analytics to maintain thousands of conveyor belts across its fulfillment centers.
DHL applies IoT-driven maintenance to keep automated guided vehicles (AGVs) online.
Manufacturers with heavy machinery use predictive monitoring to reduce costly production stoppages.
The Future of Predictive Maintenance
AI-enhanced models that self-learn from new data.
Digital twins that simulate equipment performance.
5G-enabled IoT sensors for real-time monitoring.
Blockchain-backed service logs for transparent compliance records.
Conclusion
Predictive maintenance is no longer optional—it’s a competitive advantage. By reducing downtime, extending equipment life, and enhancing safety, predictive strategies enable warehouses to cut costs and operate more efficiently. Companies that adopt predictive maintenance today will avoid costly surprises tomorrow.