Warehouse Security: Strategies, Systems & Best Practices for 2026
Warehouse security is increasingly critical as facilities become high-value targets. Rising theft, organized retail crime, and cyberattacks on connected systems make protection a boardroom issue—not just a facility manager’s concern. The right strategy reduces risk, improves insurance standing, and builds customer trust. This is why warehouse security should never be overlooked.
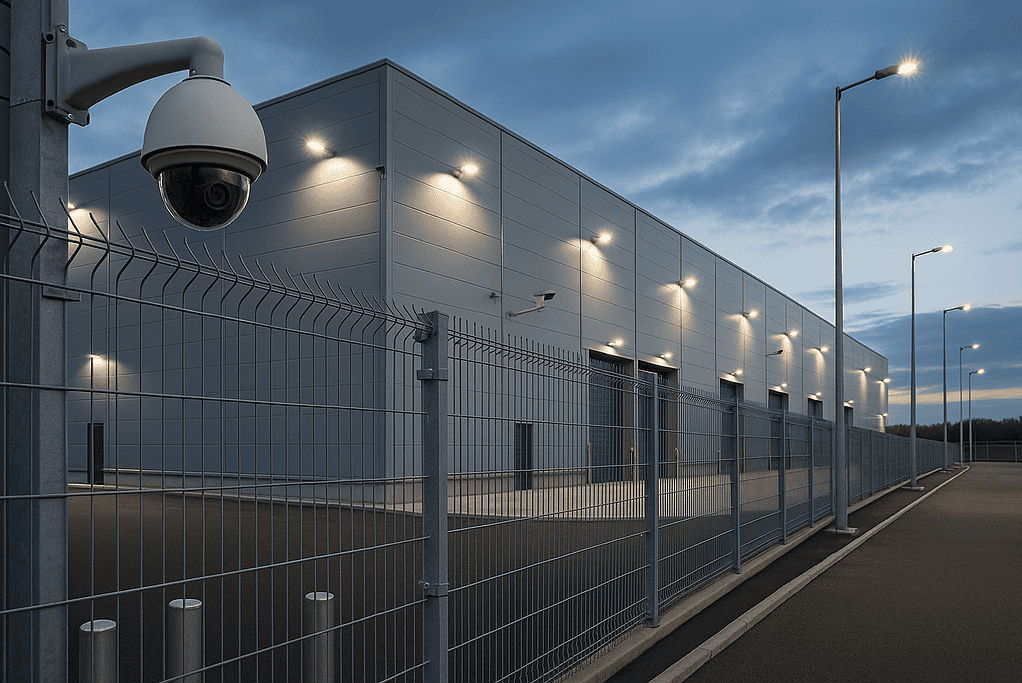

Key Components of Warehouse Security
1. Perimeter Security
Fencing, gated entry, and well-lit exteriors deter trespassers.
Bollards and barriers prevent vehicle ramming.
Landscaping should never obstruct sight lines for cameras or guards.
2. Access Control Systems
Badge or biometric entry prevents unauthorized access.
Visitor check-in systems keep a real-time log of entries.
Tiered permissions restrict high-value areas (cages, IT rooms, pharmaceuticals).
3. Surveillance and Monitoring
IP cameras with motion detection and cloud storage.
PTZ cameras cover blind spots and yard operations.
AI-enabled analytics detect unusual activity, such as loitering or forced entry.
4. Alarms and Intrusion Detection
Glass-break sensors, door contacts, and motion detectors.
Integration with local authorities or private monitoring firms ensures a rapid response.
Audible alarms serve as deterrents, while silent alarms enhance capture rates.
5. Lighting Systems
LED high-bay lighting ensures visibility inside.
Exterior LED floodlights eliminate dark zones.
Motion-activated lights conserve energy while enhancing deterrence.
6. Cybersecurity in the Warehouse
Modern warehouses use WMS, RFID, IoT sensors, and cloud platforms. Protecting these systems is as important as locking the doors.
Strong firewalls and encryption for data.
Role-based access in software.
Regular patching and phishing training for staff.

Best Practices for a Secure Warehouse
Conduct Security Audits: Regular inspections identify gaps in physical and digital systems.
Employee Training: Workers should be familiar with protocols for handling visitors, recognizing suspicious behavior, and responding to emergencies.
Segregation of Duties: Avoid giving one person total control over valuable inventory or data.
Incident Reporting: Encourage quick reporting of theft, safety breaches, or system malfunctions.
Insurance & Compliance: Meeting OSHA and insurance security requirements can reduce premiums and liability.
The Cost of Poor Security
Theft and shrinkage reduce profit margins.
Safety risks can harm staff morale and lead to legal exposure.
A single cyberattack on WMS or shipping systems can halt operations for days.
Future Trends in Warehouse Security
AI-driven video monitoring that flags abnormal activity without human supervision.
Drone patrols inside large DCs or exterior yards.
Biometric verification is becoming standard in high-value sectors.
Smart locks and IoT sensors integrated into enterprise WMS.
Key Takeaway
Warehouse security is no longer optional—it’s a competitive differentiator. By combining physical barriers, smart technology, cybersecurity, and well-trained people, operators can protect assets, improve compliance, and ensure business continuity.