Pallet in Warehouse: Comprehensive Guide to Types and Uses in 2026
In the bustling warehousing world, pallets are the unsung heroes that keep operations running smoothly. But with so many options and considerations, how do you choose the right pallet in warehouse for your needs?
Key Takeaways
- Variety of Pallet Types: Understanding the different types of pallets—wooden, metal, plastic, cardboard, and standardized Euro pallets.
Importance of Proper Loading: Properly loading pallets ensures stability and safety.
Efficient Storage Management: Effective pallet storage and management, including pricing structures, pallet spaces, and using cost calculators.
Advanced Pallet Solutions: Advanced racking systems like selective, cantilever, drive-in, push-back, and pallet flow racking.

Pallets are the backbone of modern warehousing and logistics. These simple yet essential platforms support the storage and transport of goods, playing a crucial role in the efficiency and organization of supply chains worldwide.
In certain geographic areas, especially larger cities, pricing is often higher due to the increased demand versus supply for warehouse storage.
Pallets come in various forms, from wooden to plastic, metal to cardboard, each offering unique benefits and applications.
Join us as we unpack the importance of pallets in warehousing. We will offer practical advice and expert knowledge to help you make informed decisions for your business.
Table of Contents
Types of Pallets and Their Uses
When selecting the right pallet for your warehouse, understanding the various types and their specific uses is essential. Each type of pallet offers unique benefits and is suited to different applications. Here’s a closer look at the most common types of pallets and their uses:
Block Pallets
Block pallets can be lifted from all four directions, with the upper deck supported by twelve columns.
They can be made of wood, plastic, or metal and provide high handling efficiency.

Flat Pallets

Flat pallets are injection-molded pallets available in standard sizes.
They are used to lift goods during transportation and can be easily moved using forklifts, loaders, or jacks.
Wooden Pallets
Wooden pallets are the most traditional and widely used pallets in the warehousing industry. They are valued for their durability, affordability, and ease of repair.
Wooden pallets are suitable for various applications, from heavy-duty storage to general transportation. They can be customized in size and design, making them versatile for different load requirements.
However, they are susceptible to moisture and can splinter, requiring regular maintenance.
Common Uses:
Heavy goods storage
General warehousing
Export shipments (with heat treatment for pest control)
Metal Pallets
Metal pallets, typically made from steel or aluminum, are known for their exceptional strength and longevity. They are ideal for environments where hygiene and sterility are critical, such as pharmaceutical and food industries.

Metal pallets can withstand extreme temperatures and resist damage from chemicals and moisture, making them a reliable choice for heavy and hazardous materials.
Common Uses:
High-value goods storage
Hazardous materials handling
Cleanroom environments
Plastic Pallets

Plastic pallets offer a lightweight yet durable alternative to wooden and metal pallets. They are resistant to moisture, chemicals, and insects, making them an excellent choice for industries requiring stringent hygiene standards.
Plastic pallets are easy to clean and sanitize, and they do not splinter or have protruding nails, reducing the risk of product damage and worker injury.
Additionally, plastic pallets are highly beneficial in the food processing industry for both indoor and outdoor storage, as well as for handling fragile products.
Common Uses:
Food and beverage industries
Pharmaceutical storage
Retail and point-of-sale displays
Cardboard Pallets
Cardboard or paper pallets are an eco-friendly, lightweight option for single-use or short-term applications. These pallets are fully recyclable and are often used for shipping lightweight goods. While not as durable as other pallet types, cardboard pallets offer significant cost savings and are easy to dispose of.

Common Uses:
Lightweight product shipping
Export shipments (disposable use)
Retail displays
Standardized Euro pallets (Sizes and Features)

Euro pallets, or Euro pallets, adhere to the European Pallet Association (EPAL) standards, ensuring uniformity in size and quality. The standardized dimensions (1200mm x 800mm) make them ideal for efficient space utilization in European warehouses and transportation systems. Europallets are typically made of wood but can also be found in plastic and metal variants.
Common Uses:
Cross-border shipments within Europe
Automated warehousing systems
Efficient space management in transport and storage
Customized Pallets for Specific Applications
Customized pallets are designed to meet specific requirements of unique applications. They can be tailored in size, material, and load capacity to suit particular products or industries.
Custom pallets provide the flexibility to accommodate unusual shapes, sizes, and weights, ensuring optimal protection and efficiency in handling.
Common Uses:
Industry-specific storage needs
Custom product handling and transportation
Specialized equipment storage
Choosing the right type of pallet for your warehouse involves considering the specific needs of your operations, the nature of the goods being stored or transported, and the environmental conditions they will be subjected to.
By understanding the strengths and applications of each type of pallet, you can make informed decisions that enhance the efficiency and safety of your warehousing activities.
Key Features and Benefits of Different Pallets

Selecting the right pallet involves understanding the material, type, and specific features and benefits that can enhance your warehouse operations.
Choosing the right pallet material for a specific inventory and considering the role of unit load in facilitating the handling and transfer of goods is crucial for efficient operations.
Here are some key features and benefits of various pallets that can help you optimize your logistics and storage processes:
Precision Pallets
Precision pallets are designed with exacting standards to ensure uniformity and consistency. This makes them ideal for automated systems where precise dimensions are crucial for smooth operation.
Precision pallets help reduce errors in material handling and improve the efficiency of automated storage and retrieval systems.
Key Benefits:
Enhanced compatibility with automated systems
Reduced risk of pallet misalignment and jamming
Improved overall operational efficiency
Lightweight Pallets with a Lower Footprint
Lightweight pallets are engineered to reduce the Weight of the pallet itself while maintaining strength and durability. They are easier to handle and transport, reducing the strain on workers and equipment.
The larger footprint means they take up less space, both in storage and during transportation, leading to cost savings in shipping and storage.
Key Benefits:
Reduced transportation costs
Easier manual handling, reducing workplace injuries
Increased storage capacity due to lower pallet footprint
Recycling Options and Green Pallets

Green pallets are designed with sustainability in mind. They are made from recyclable materials or designed for reuse and recycling at the end of their lifecycle.
These pallets help reduce environmental impact and can be part of a company’s sustainability initiatives. Plastic pallets are gaining ground as a viable alternative to wood pallets due to their durability, ease of cleaning, and recyclability.
Key Benefits:
Reduced environmental footprint
Support for sustainability goals and green certifications
Potential cost savings through reuse and recycling programs
Engineered Wood Pallets
Engineered wood pallets are made from composite wood materials and are stronger and more durable than traditional wooden pallets.
They are also less prone to warping and splintering, providing a more reliable option for heavy-duty applications. Engineered wood pallets can also be treated to resist moisture and pests, extending their lifespan.
Key Benefits:
Increased durability and longevity
Resistance to environmental factors like moisture and pests
Consistent performance under heavy loads
Pallets with Extra Protection
Pallets with extra protection features are designed to safeguard sensitive or high-value goods during storage and transportation. These pallets may include additional coatings, covers, or built-in cushioning to protect against damage from impacts, moisture, or contamination.
Key Benefits:
Enhanced protection for delicate or valuable items
Reduced risk of product damage and associated costs
Increased customer satisfaction due to better product condition upon delivery
Understanding and leveraging the key features and benefits of different pallets allows you to select the best options to meet your specific operational needs.
Whether you prioritize precision, sustainability, durability, or protection, there is a pallet solution that can help optimize your warehouse performance and contribute to a more efficient supply chain.
Pallet Storage and Management

Efficient pallet storage and management are crucial for optimizing warehouse operations and controlling costs. Understanding the intricacies of pallet storage pricing, calculating the necessary space, and using tools like cost calculators can significantly enhance your warehousing strategy.
Pallet Storage Pricing and Warehouse Storage Explained
Pallet storage pricing involves various factors, including the type of storage (short-term vs. long-term), the nature of the goods, and the storage environment (e.g., temperature-controlled, dry storage).
Warehouses may charge based on the number of pallet positions, cubic footage, or a combination. Differentiating between personal storage and commercial warehouse storage services is crucial, as businesses have various types of warehouse services available to meet their specific needs.
Knowing how these costs are structured helps plan and budget warehouse operations.
Key Considerations:
Type of Storage: Short-term vs. long-term, temperature-controlled vs. ambient
Nature of Goods: Fragility, perishability, special handling requirements
Space Utilization: Efficient use of space can reduce overall costs
Rates, Fees, Costs, and Prices of Pallet Storage
The costs associated with pallet storage can vary widely depending on several factors. These include geographic location, the specific services required (handling, packaging, and transportation), and the warehouse’s pricing model. Understanding these rates and fees is essential for effective cost management.
Factors Affecting Costs:
Geographic Location: Urban vs. rural, proximity to transport hubs
Additional Services: Handling, packaging, transportation, and value-added services
Warehouse Type: Public vs. private warehouses, specialized storage facilities
Calculating the Number of Pallet Spaces Needed
Calculating the number of pallet spaces required is critical for optimizing warehouse storage. This involves understanding the dimensions of your pallets, the storage configuration, and the overall volume of goods.
Proper calculation ensures you rent or allocate the right space, avoiding underutilization or overextension of resources. Additionally, selecting the right storage system for specific inventory is essential to maximize resources and protect the inventory.
Steps to Calculate:
Measure Pallet Dimensions: Length, width, and height
Determine Storage Configuration: Single-deep, double-deep, block-stacking, or racking
Calculate Volume: Total volume of goods to be stored divided by the volume per pallet
Pallet Storage Cost Calculator
Using a pallet storage cost calculator can simplify estimating your storage expenses. These calculators consider various factors, such as the number of pallets, storage duration, and additional services, to provide a comprehensive cost estimate. Utilizing these tools helps in making informed financial decisions and improving budget accuracy.
Using the Calculator:
Input Parameters: Number of pallets, storage duration, type of storage, additional services
Analyze Results: Compare different scenarios and options to find the most cost-effective solution
Plan Budget: Use the estimated costs to plan and allocate your storage budget effectively
By mastering the aspects of pallet storage and management, including understanding pricing structures, calculating space needs, and utilizing cost calculators, you can optimize your warehouse operations, reduce costs, and improve overall efficiency. This comprehensive approach ensures that your pallet storage strategy aligns with your business goals and operational requirements.
Pallet Handling and Optimization in Warehouses

Efficient pallet handling and optimization are fundamental to maintaining smooth warehouse operations. Proper loading techniques, strategic order preparation, and managing damaged racking systems effectively can significantly enhance productivity and safety.
How to Load a Pallet Properly
Properly loading a pallet is essential to ensuring the stability and safety of the goods during storage and transport. Proper loading techniques help prevent product damage and reduce the risk of accidents.
Steps for Proper Loading:
Distribute Weight Evenly: Ensure the Weight is evenly distributed across the pallet to maintain balance.
Stacking Patterns: Use a brick or column stacking pattern to provide stability.
Securing Loads: Use stretch wrap, straps, or shrink wrap to secure the load and prevent shifting.
Height and Weight Limits: Adhere to height and weight limits to avoid overloading and potential tipping.

Recommendations for Loading Goods on Pallets
Following best practices for loading goods on pallets can improve efficiency and safety in your warehouse operations.
Best Practices:
Standardize Pallet Sizes: Use standardized pallet sizes to streamline handling and storage.
Label Clearly: Clearly label each pallet with relevant information for easy identification.
Use Protective Materials: Use corner protectors, slip sheets, and padding to safeguard goods.
Training: Ensure staff are trained in proper loading techniques and safety protocols.
Warehouse Order Preparation and Optimization
Efficient warehouse order preparation and optimization are key to meeting customer demands and maintaining high service levels.
Strategies for Optimization:
Picking Methods: To speed up order fulfillment, utilize efficient picking methods such as batch picking, zone picking, or wave picking.
Slotting: Optimize slotting by placing high-demand items in easily accessible locations.
Technology: Implement warehouse management systems (WMS) to automate and streamline order processing.
Regular Audits: Conduct regular audits to identify and address inefficiencies in the order preparation.
Dealing with Damaged Warehouse Racking

Damaged warehouse racking can pose serious safety hazards and disrupt operations. It’s crucial to address and repair any damage promptly.
Steps to Manage Damaged Racking:
Regular Inspections: Conduct regular inspections of racking systems to identify damage early.
Report and Repair: Report any damage immediately and arrange for repairs as soon as possible.
Safety Protocols: Implement safety protocols to prevent damage, such as proper forklift operation and weight limits.
Reinforcement: Consider reinforcing racking systems in high-traffic areas to reduce the risk of damage.
By adhering to best practices for pallet handling, optimizing order preparation, and effectively managing damaged racking, warehouses can enhance operational efficiency, ensure safety, and provide better service to customers. These strategies are vital for maintaining a well-organized and productive warehouse environment.
Selective Pallet Racking

Selective pallet racking is the most common and versatile type of racking system. It allows direct access to each pallet, making it ideal for warehouses with many products and high turnover rates.
Key Benefits:
Direct Access: Easy access to each pallet without moving others.
Flexibility: Suitable for various pallet sizes and types.
Cost-Effective: Relatively low cost and easy to install.
Cantilever Racking
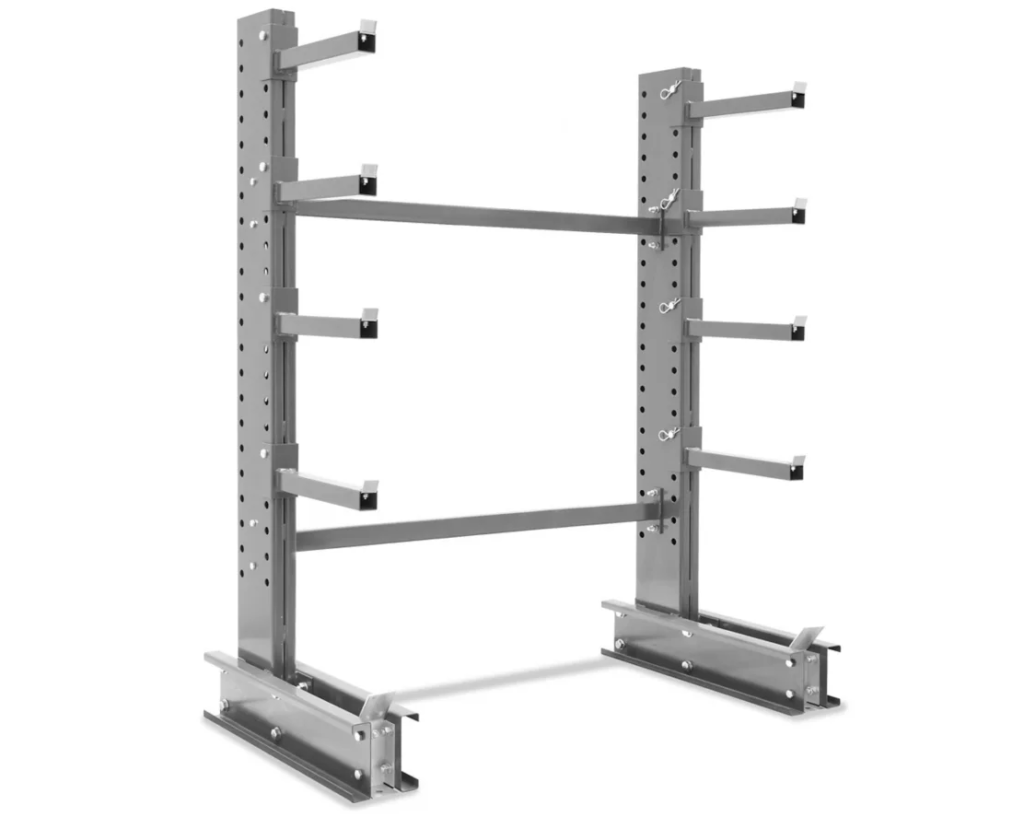

Cantilever racking is designed to store long, bulky items such as lumber, pipes, and furniture. It consists of arms extending from a central column, providing open access without vertical obstructions.
Key Benefits:
Versatility: Ideal for storing long and irregularly shaped items.
Accessibility: Easy loading and unloading from the front without vertical columns.
Adjustable: Arms can be adjusted to accommodate different item sizes.
Drive-In Pallet Racking
Drive-in pallet racking allows forklifts to drive directly into the rack’s lanes, enabling high-density storage. This system is suitable for storing large quantities of homogeneous products.
Key Benefits:
High Density: Maximizes storage space by eliminating aisles.
Cost Savings: Lower storage costs per pallet position.
FIFO/LIFO: Suitable for first-in, first-out (FIFO) and last-in, first-out (LIFO) inventory systems.
Push-Back Pallet Racking
Push-back racking systems use a series of nested carts on inclined rails. Pallets are loaded from the front and pushed back, allowing for high-density storage with multiple pallet positions deep.
Key Benefits:
Efficient Space Utilization: Higher storage density compared to selective racking.
Accessibility: Easier access to different SKUs from the front.
FIFO/LIFO: Supports both FIFO and LIFO inventory methods.
Pallet Flow Pallet Racking
Pallet flow racking, or gravity flow racking, uses sloped shelves with rollers to allow pallets to move forward automatically as the front pallet is removed. This system is ideal for high-turnover products.
Key Benefits:
High Throughput: Ideal for high-volume operations with fast-moving products.
Space Efficiency: Maximizes storage space and improves picking efficiency.
FIFO: Ensures first-in, first-out inventory management.
Temperature Controlled Pallet Warehouses
Temperature-controlled pallet warehouses are essential for storing perishable goods, pharmaceuticals, and other temperature-sensitive items. These warehouses maintain specific temperature ranges to ensure product quality and safety.
Key Benefits:
Product Integrity: Maintains the quality and safety of temperature-sensitive goods.
Regulatory Compliance: Meets industry regulations for storing perishable and sensitive products.
Flexibility: Can be adapted to different temperature requirements, such as refrigerated, frozen, or climate-controlled environments.
Conclusion: Pallet in Warehouse
Choosing the right racking systems and specialized storage environments, you can optimize your warehouse space, enhance safety, and meet your business’s specific needs.