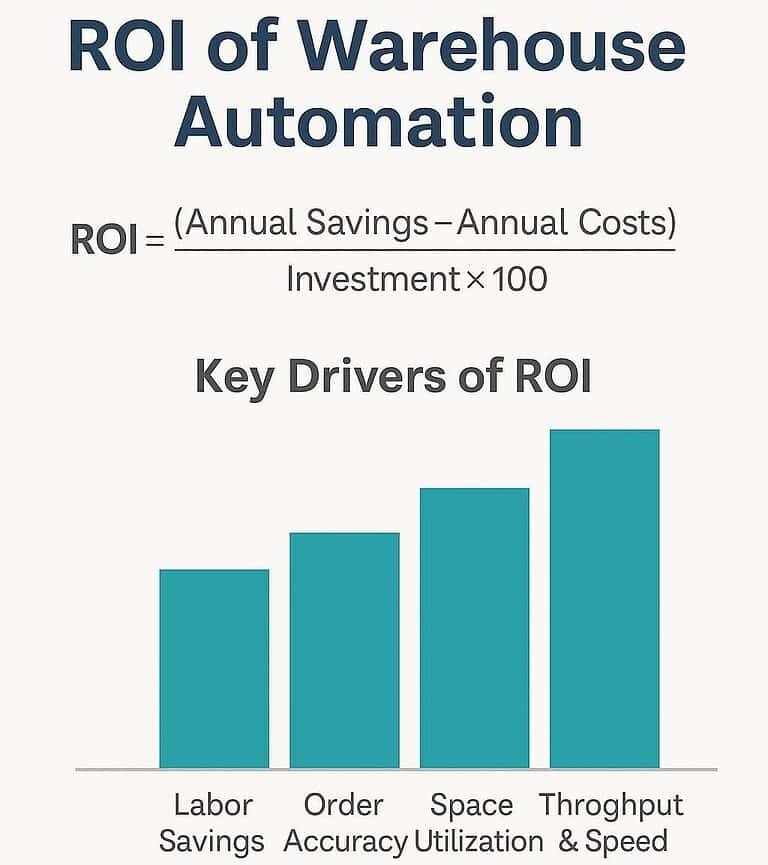
Warehouse Best Practices: Next-Level Efficiency Ideas for 2026
Warehouses today are under more pressure than ever: labor shortages, rising costs, customer expectations for speed, and constant change in technology. “Good enough” warehouse best practices won’t cut it anymore.
This guide is for operators ready to move beyond outdated work instructions and into formal, scalable, and future-proof strategies. These aren’t just tips — they’re next-level practices built for 2025 and beyond.

Why Best Practices Matter in 2025
Best practices aren’t box-checking exercises for compliance. They’re the foundation of efficiency, safety, and profitability. When applied consistently, they:
Reduce wasted labor and bottlenecks.
Improve safety and morale.
Free up capital by controlling inventory smarter.
Build resilience against disruptions.
And here’s the truth: the practices that worked 10 years ago aren’t enough anymore. Let’s break down the next-level strategies that matter now.
1. Productivity and Flow: Kill Bottlenecks Before They Start
Workforce Optimization
Use labor management tools to match staffing to demand by the hour, not just the day.
Pro Tip: Ask IT for the total number of orders dropping into the warehouse by hour across a full week. You’ll see exactly where you’re under- or over-staffed.
Labor Management Systems (LMS)
Track individual and team performance, not to punish but to pinpoint training and re-slotting opportunities.
Suggest efficient pick paths to cut down wasted travel time.
Benchmarking
Don’t operate in a vacuum. Compare against industry metrics, such as picks/hour, order cycle time, and error rate.
Sources: WERC, CSCMP, software vendor reports, and peer groups.
Warehouse Layout and Flow
One-touch order picking: design routes so items for multiple orders can be grabbed in a single pass.
Slotting: keep fast movers near pack-out; store slow movers high or further away.
Apply 5S: Sort, Straighten, Shine, Standardize, Sustain. A clean, organized warehouse is always more productive.

2. Inventory and Data: Stop Tying Up Capital
Real-Time Inventory Visibility
Outdated spreadsheets belong in the past. A modern WMS gives you instant insight into what’s in stock, what’s low, and what’s moving.
Smart Inventory Controls
ABC Analysis: Prime space for “A” items, long-term storage for “C” items.
Cycle Counting: Audit continuously instead of waiting for year-end chaos.
AI and Forecasting
AI-enhanced demand forecasting reduces stockouts and prevents excess inventory.
Predictive models give suppliers visibility, so they can plan without endless calls or emails.
The point: inventory is capital. Managing it with outdated tools ties up cash and adds risk.
3. Workforce and Safety: Protect People, Boost Performance
Culture of Safety
Safety isn’t compliance — it’s culture. When workers feel safe, productivity rises.
Leadership must show visible commitment.
Encourage open reporting without fear.
Invest in real training, not just a check-the-box module.
Safety Programs
Regular inspections and preventative maintenance reduce accidents and downtime.
Emergency plans should be practiced, not just posted.
Technology for Safety
AI-powered cameras can detect blocked aisles, missing PPE, or unsafe lifts in real time.
Wearables and IoT sensors can monitor ergonomics and environmental hazards.
Your workforce is the warehouse engine. Invest in them, keep them safe, and efficiency follows.
4. Technology and Automation: Smarter Tools, Not Just More Tools
Warehouse Management Systems (WMS)
Your WMS is the nervous system of operations. It should provide:
Real-time stock visibility.
Optimized pick/putaway paths.
Integrated labor scheduling.
Emerging Tech
AI: Forecast demand, flag safety risks, and optimize slotting daily.
IoT: Sensors track inventory, equipment health, and environmental conditions.
Robotics: Handle repetitive tasks like palletization or transport, freeing humans for higher-value work.
AR: Glasses or handhelds that guide pickers visually to the right item, reducing errors.
Pro Tip: Don’t chase tech for the buzz. Pick tools that solve your actual bottlenecks and scale with you.
5. Sustainability and Maintenance: Efficiency That Pays
Eco-efficiency isn’t just about being green — it saves money.
LED lighting slashes energy bills.
Preventive maintenance keeps equipment alive longer and reduces downtime.
Reusable packaging + recycling programs cut waste and costs.
Optimized transportation reduces fuel spend and carbon footprint.
The warehouses leading in sustainability will also be leading in cost efficiency.

6. Continuous Improvement: From Projects to Culture
Here’s the hard truth: process improvement projects as we’ve known them are outdated. By the time a project wraps, the process has already shifted.
The New Model
Continuous evaluation with real-time data.
Kaizen and Six Sigma for daily improvements, not annual reviews.
AI as the new “continuous improvement engine” — adapting midstream instead of months later.
Future Focus
Expect more robotics and automation.
Augmented reality for training and picking.
AI-driven labor planning.
Improvement isn’t a one-time initiative. It’s the culture you build.
The Road to Excellence
Warehouse best practices in 2025 are about more than just efficiency. They’re about resilience, adaptability, and staying competitive in a world where change is the only constant.
The path forward is clear:
Optimize productivity and flow.
Treat inventory as capital.
Protect and empower your workforce.
Adopt smart, scalable technology.
Invest in sustainability.
Build a culture of continuous improvement.
Do these consistently, and your warehouse won’t just keep up — it will set the pace.

FAQ Section
What are the most important warehouse best practices for 2025?
The top best practices include optimizing warehouse flow, treating inventory as a capital asset, investing in workforce safety, adopting scalable technology, and prioritizing sustainability.
How does AI improve warehouse best practices?
AI supports real-time decision-making for inventory forecasting, labor scheduling, safety monitoring, and slotting. It serves as a continuous improvement engine that adapts more quickly than traditional methods.
Why is sustainability a warehouse best practice?
Sustainability reduces energy use, waste, and costs while meeting regulatory and customer expectations. Eco-efficiency also extends equipment life and improves profitability.
How do you measure warehouse best practice success?
Success can be tracked through KPIs like picks per hour, order accuracy, on-time shipments, inventory turnover, and safety incident rates. Benchmarking against industry data helps validate results.