Cold Storage Warehousing: Design, Costs & Best Practices
Cold storage warehousing is one of the most specialized—and costly—areas of the supply chain. From frozen foods to pharmaceuticals, businesses depend on cold storage to preserve product quality and comply with strict regulations. However, the complexity of designing, operating, and maintaining these facilities presents a challenge for even experienced warehouse professionals.
This guide explores the definition, types, design considerations, technology trends, and best practices in cold storage warehousing.
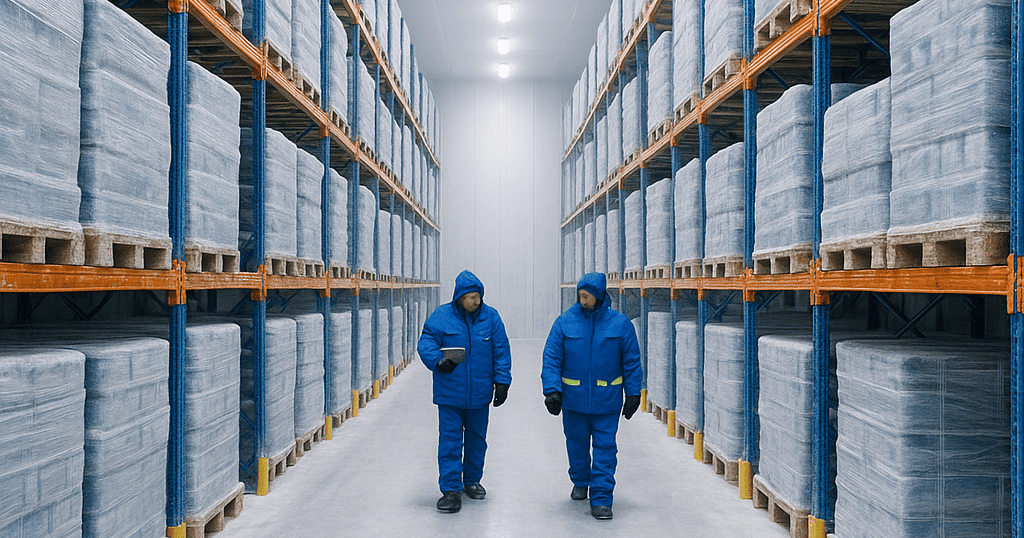

What is Cold Storage Warehousing?
Cold storage warehouses are temperature-controlled facilities designed to store perishable goods. They differ from standard warehouses in that they:
Operate across temperature ranges (frozen, chilled, ambient).
Require specialized insulation, flooring, and doors.
Use advanced refrigeration and monitoring systems.
Types of Cold Storage Facilities
Frozen Storage → -10°F to -20°F, for meat, seafood, ice cream.
Chilled Storage → 32°F to 50°F, for produce, dairy, and beverages.
Pharmaceutical Cold Chain → 36°F to 46°F, for vaccines and biologics.
Blast Freezers → Rapid cooling for freshly processed food.
Key Design Considerations
Insulation & Construction: Walls, doors, and flooring designed to prevent heat intrusion.
Material Handling: Cold-rated forklifts, low-temp lubricants, and anti-slip flooring.
Racking & Layout: Drive-in/drive-thru racking for dense storage; minimize door openings.
Energy Efficiency: LED lighting, variable-speed compressors, and high-speed doors.

Cost Factors in Cold Storage
Cold storage facilities can cost 2–3x more to build and operate than ambient warehouses due to:
Specialized construction.
High energy consumption.
Continuous maintenance of refrigeration systems.
Smaller labor pool (working conditions are difficult).
ROI is achieved through lower spoilage, extended shelf life, and compliance with regulations.
Technology in Cold Storage Warehousing
Warehouse Management Systems (WMS): Integrate with sensors for temperature monitoring.
Automated Storage & Retrieval Systems (AS/RS): Reduce labor exposure to freezing conditions.
IoT Sensors & Data Logging: Real-time monitoring for compliance.
Backup Generators: Essential for Preventing Catastrophic Product Loss.
Best Practices for Cold Storage Operations
Minimize Door Openings: Use high-speed doors and air curtains.
Train Staff: Workers must rotate to avoid fatigue in cold environments.
Regular Maintenance: Keep refrigeration equipment running efficiently.
Safety Protocols: Slips, trips, and frostbite are major risks.
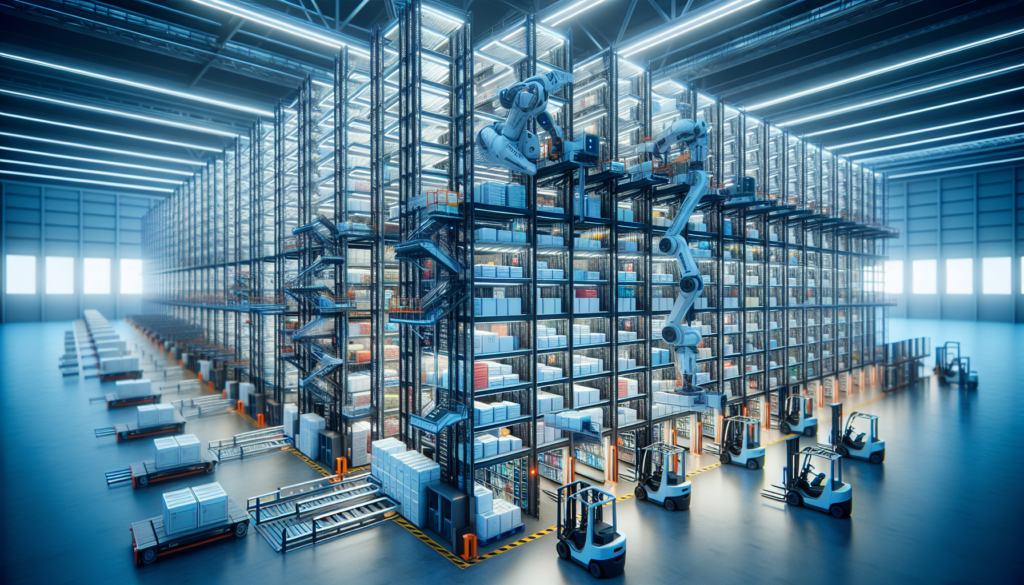

Future Trends
Robotics in Cold Storage: AMRs and AS/RS reduce human exposure to extreme cold.
Sustainable Refrigerants: Transition to Eco-Friendly Gases to Meet Global Compliance.
Energy Recovery Systems: Cutting costs in high-energy environments.
Dark Freezer Warehouses: Fully automated, lights-out facilities
Key Takeaway
Cold storage warehousing is mission-critical for perishable supply chains, but it comes at a premium. With the right design, technology, and best practices, businesses can balance cost, safety, and compliance while ensuring product integrity.
Additional Resources
Regulatory & Compliance (for food & pharma cold chain)
- U.S. FDA – Food Safety & Cold Chain Requirements
- CDC – Vaccine Storage & Handling (for pharmaceutical cold chain)
Industry Associations
- Global Cold Chain Alliance (GCCA) – Resources and best practices
- IInternational Association of Refrigerated Warehouses (IARW) – Cold storage trends